eProcurement System (SAP-SRM) Testing
The Government of India acknowledges that automating procurement process using electronic tools/techniques and enabling opportunities to suppliers fully supports the objective of non‐discrimination, fair & open competition. eProcurement is identified as a mission mode project under national governance plan. The objective is to transform public sector purchase activity from labor intensive paper based to efficient eProcurement process. Use of Information Technology promotes the aims of open, non‐discriminatory and efficient government procurement through transparent procedures.
The factors driving the adoption of eProcurement are:
- Reduced purchasing cost and improved efficiency
- Standardized purchasing processes across the organization
- Reduced administrative costs with better effectiveness
- Significant reduction in the procurement cycle
- Reduced discretion
At the same time the inhibitors to adoption are:
- Lack of supplier readiness
- System integration issues (compatibility and interoperability)
- Confidence on the system (Security, Functionality and Performance)
- Insufficient skilled staff
The essential quality characteristics of eProcurement system cover Security, Transparency & Functionality.
General Requirements of eProcurement System
The basic requirements of any eProcurement system are to achieve the goal of Government procurement, standardization of procurement processes and information entities in an efficient and transparent way. Hence the key requirements are to:
Address the requirement of GFR
For public procurement of goods, services, works (e.g. construction) compliance with GFR rules, processes, roles (purchasing officer, local purchasing committee etc) are mandatory requirements. The GFR rules needs to be applied into the application workflow of e‐tendering process. eProcurement System should be designed as per defined workflow with adequate security measures.
Confidentiality and Integrity of Information
The key requirement of procurement in public service organisation is to maintain the confidentiality & integrity of the information in procurement life cycle to protect the interest of buyer & supplier and to encourage the competitiveness in the business. The e‐procurement platform transacts confidential procurement data and is exposed to several security threats. This requires employing a combination of security technologies and security best practices which result in reduced threat of data loss, leakage or manipulation.
Address Vigilance Guidelines
The system should meet the requirements of guidelines issued from time to time by Central Vigilance Commission.
System Adaptability & customisation
eTendering System need to have templates to offer flexibility in bidding methodologies as prevailing and followed currently in the manual process. Further, system should have templates to adopt bidding methodologies as may be prescribed by respective authorities.
Objective
Assuring Quality and Security of an e‐Procurement system so that confidence can be provided to its stakeholders that the system is secure, transparent, auditable & compliant with government procurement procedures.
Approach
To achieve the above objective the following approach is recommended.
- Evaluation of eProcurement System (including data, software, hardware, network, process) to ensure
- Correct & complete implementation of organisation procurement policies & procedures
- Compliance to GFR rules, CVC guidelines, IT Act (including amendments)
- Assuring Security by Design & Development (ie some critical security and transparency related functionality has to be built into the e‐procurement software application) , Implementation, Deployment & Use
- Security of Data Storage and Communication
- Performance
- Usability
- Interoperability
- Identification of risks and concerns of e‐procurement system & providing the guidelines for mitigating the identified risks.
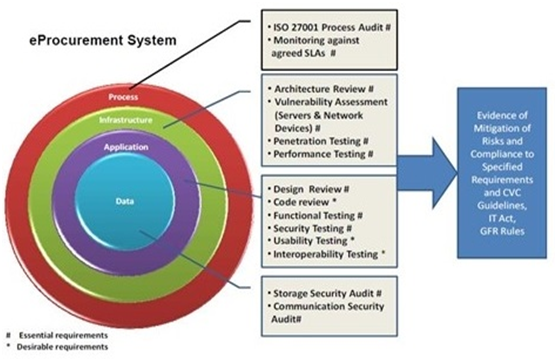
eProcurement Quality and Security Assurance Model
A eProcurement Quality and Security Assurance Model is depicted below